Superpowers face off in the cold war 49a answer key – Superpowers Face Off in the Cold War: 49A Answer Key provides a comprehensive overview of the key events, strategies, and outcomes of the Cold War, a period of intense rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union that shaped the 20th century.
This answer key offers a structured approach to understanding the origins, evolution, and impact of the Cold War, making it an invaluable resource for students and researchers seeking a deeper understanding of this pivotal period in world history.
Historical Context

The Cold War emerged after World War II as a prolonged state of political and military tension between the United States and its Western allies, and the Soviet Union and its Eastern bloc allies.
The origins of the Cold War can be traced to ideological differences between the two superpowers, particularly the contrasting political and economic systems of capitalism and communism.
Key Players and Ideologies
- United States:Capitalist democracy, leader of the Western bloc
- Soviet Union:Communist state, leader of the Eastern bloc
Superpower Rivalry
Two Superpowers
- United States:Economically and militarily dominant, advocate of containment
- Soviet Union:Ideologically driven, sought to expand communist influence
Political, Economic, and Military Strategies
- United States:Containment policy, economic aid to allies, military alliances (NATO)
- Soviet Union:Expansionist policies, economic planning, military buildup
Nuclear Arms Race
Development and Impact of Nuclear Weapons
The development of nuclear weapons during the Cold War had a profound impact on international relations.
Nuclear weapons became the ultimate symbol of power and deterrence, leading to a constant race between the superpowers to build larger and more sophisticated arsenals.
Nuclear Strategies and Doctrines
- United States:Massive retaliation, flexible response
- Soviet Union:Assured destruction, preemptive strike
Proxy Wars and Alliances: Superpowers Face Off In The Cold War 49a Answer Key
Major Proxy Wars and Alliances
- Korean War (1950-1953):US-backed South Korea vs. Soviet-backed North Korea
- Vietnam War (1955-1975):US-backed South Vietnam vs. Soviet-backed North Vietnam
- NATO (1949):Western military alliance led by the US
- Warsaw Pact (1955):Eastern bloc military alliance led by the Soviet Union
Motivations and Strategies
Superpowers used proxy wars and alliances to gain influence, contain their rivals, and expand their spheres of influence.
Cultural and Ideological Confrontation
Ideological and Cultural Differences
- Capitalism:Free market, individual liberty
- Communism:Centralized planning, collective ownership
Propaganda and Cultural Exchanges
Superpowers engaged in extensive propaganda campaigns to promote their ideologies and discredit their rivals.
Cultural exchanges, such as art exhibitions and sporting events, were also used to shape public opinion.
Crisis Points and Détente

Major Crisis Points
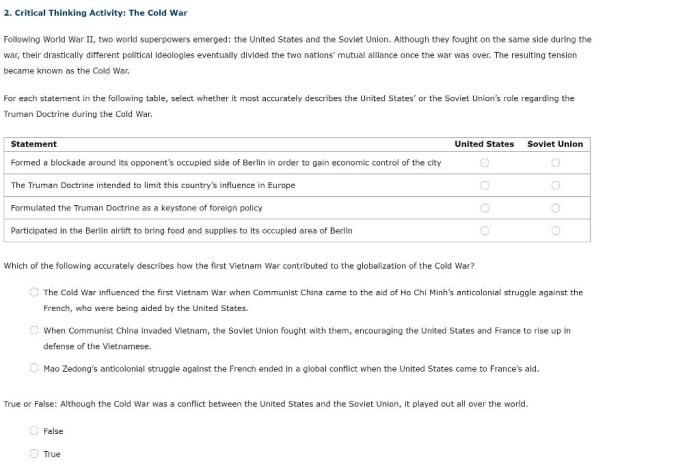
- Berlin Blockade (1948-1949)
- Cuban Missile Crisis (1962)
Periods of Détente
- 1970s:Strategic Arms Limitation Treaty (SALT)
- 1980s:Nuclear disarmament negotiations
Factors Contributing to Crisis Points and Détente
Crisis points were often triggered by aggressive actions or misunderstandings between the superpowers.
Détente was facilitated by a combination of factors, including the threat of nuclear war, economic pressures, and the rise of new leaders.
The End of the Cold War

Factors Leading to the End, Superpowers face off in the cold war 49a answer key
- Economic stagnation in the Soviet Union
- Glasnost and perestroika reforms
- US pressure and containment policy
Key Individuals and Events
- Mikhail Gorbachev:Soviet leader who implemented glasnost and perestroika
- Ronald Reagan:US President who pursued a hardline stance against the Soviet Union
- Fall of the Berlin Wall (1989):Symbolic event marking the end of Soviet control over Eastern Europe
Answers to Common Questions
What were the key factors that led to the outbreak of the Cold War?
Ideological differences between the United States and the Soviet Union, the rise of communism in Eastern Europe, and the aftermath of World War II.
How did the nuclear arms race shape the Cold War?
It created a balance of terror, fueled tensions, and led to the development of strategies like Mutually Assured Destruction (MAD).
What were the major proxy wars during the Cold War?
Korean War, Vietnam War, and the Soviet-Afghan War.
What was the significance of the Cuban Missile Crisis?
It brought the world to the brink of nuclear war and highlighted the need for diplomacy and crisis management.
What factors contributed to the end of the Cold War?
Economic and political reforms in the Soviet Union, the rise of Mikhail Gorbachev, and the collapse of communist regimes in Eastern Europe.
