Identify effective techniques for accurate pipet use. Embark on a comprehensive journey into the realm of precision pipetting, where we unravel the secrets of meticulous liquid handling, empowering you with the knowledge and skills to achieve unparalleled accuracy and reliability in your laboratory endeavors.
Delve into the intricacies of pipette selection, calibration, and maintenance, gaining a profound understanding of the factors that influence precise volume measurement and delivery. Discover the nuances of aspirating and dispensing liquids, mastering the techniques for handling diverse liquid properties, and explore specialized pipetting methods that elevate your experimental capabilities.
Essential Techniques for Accurate Pipette Use
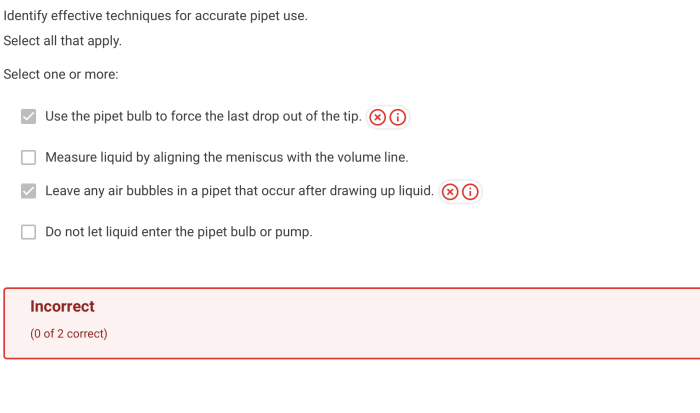
Accurate pipetting is crucial in various scientific and laboratory applications. Mastering the essential techniques is paramount for reliable and precise measurements. These techniques include proper grip, posture, and selecting the appropriate pipette for the task. Regular pipette calibration and maintenance are also essential to ensure accurate volume delivery.
Selecting the Appropriate Pipette
- Consider the volume range and accuracy required for the task.
- Choose pipettes with clear and legible graduations.
- Select pipettes with ergonomic designs for comfortable handling.
li>Ensure the pipette is compatible with the type of liquid being dispensed.
Volume Measurement and Delivery
Pipettes have different types of volume measurement scales, including digital, analog, and gravimetric. Accurate volume delivery involves reading the meniscus correctly. The meniscus is the curved surface of the liquid in the pipette tip. It should be aligned with the graduation mark for precise volume measurement.
Techniques for Avoiding Errors
- Avoid parallax by holding the pipette at eye level and reading the meniscus from the side.
- Minimize evaporation by keeping the pipette tip immersed in the liquid.
- Dispense the liquid slowly and smoothly to prevent droplets from forming.
Liquid Handling Techniques
Proper liquid handling techniques ensure accurate volume delivery. Air displacement pipettes use a piston to create a vacuum that draws liquid into the tip. Positive displacement pipettes use a plunger to directly displace the liquid.
Handling Special Liquids
- For viscous liquids, use pipettes with wide-bore tips.
- For volatile liquids, minimize exposure to air by aspirating and dispensing quickly.
- For liquids with high surface tension, use pipettes with hydrophobic tips.
Advanced Pipetting Techniques, Identify effective techniques for accurate pipet use.
Specialized pipetting techniques include reverse pipetting and multi-channel pipetting. Electronic pipettes and automated pipetting systems offer increased accuracy and efficiency.
Reverse Pipetting
In reverse pipetting, liquid is aspirated beyond the desired volume and then dispensed to the exact mark.
Multi-Channel Pipetting
Multi-channel pipettes allow for simultaneous aspiration and dispensing of multiple samples, increasing throughput.
Electronic Pipettes
Electronic pipettes provide precise and repeatable volume delivery with digital displays and calibration features.
General Inquiries: Identify Effective Techniques For Accurate Pipet Use.
What are the common errors to avoid in pipetting?
Parallax errors, evaporation, and improper pipette selection can lead to inaccuracies in pipetting.
How do I handle viscous liquids with a pipette?
Use a wide-bore pipette tip and dispense the liquid slowly to minimize shear forces.
What is the difference between air displacement and positive displacement pipettes?
Air displacement pipettes use a piston to create a vacuum that aspirates liquid, while positive displacement pipettes use a plunger to directly displace liquid.